Food adulteration. Everybody has heard about it. We have read numerous articles online and in the local Daily about the police confiscating x and y quantities of adulterated fish or milk or other food items. Is food adulteration as simple as adding water to milk to increase the quantity, or something more? Something more nefarious?
Food adulteration is defined as the act or process of intentionally or willingly degrading the quality of food items offered for sale either by the addition or substitution of inferior substances or by the removal of some valuable ingredient/s to increase the shelf life or to make it look more appealing in the eyes of the prospective customer. With retailers and sellers eyeing profit over quality, the cases of adulteration in food has increased multi-fold over the last decade.
Food Contamination is food that has been corrupted by another substance intentionally or unintentionally. This could be
- Physical contamination, which is when a foreign object contaminates food. This can happen at any stage of the production process and include Band-Aids, steel, wool or pieces of plastic.
- Biological contaminants are produced by humans, rodents, insects or microorganisms.
- Chemical contaminants may be natural or artificial such as chemical substances like pesticides
The Epidemiology of the Problem
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India has found a consistent increase in food adulteration cases in the country over the past few years.
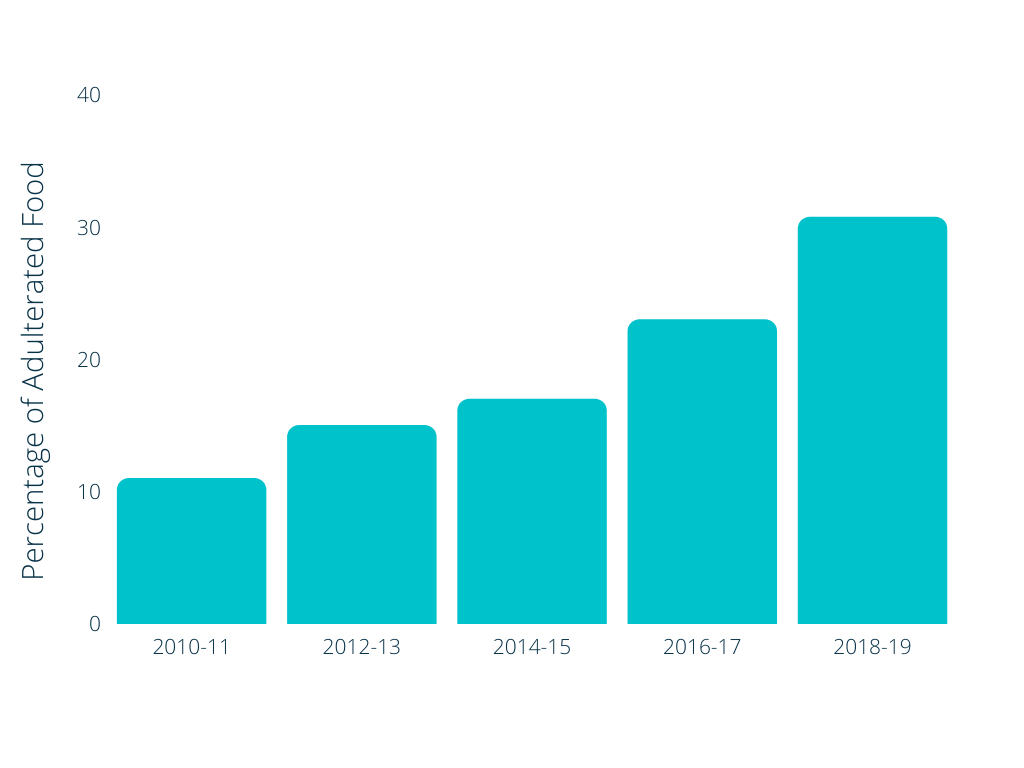
As per a report by ET, Minister for Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution Ram Vilas Paswan, stated that between 2016-17 and 2018-19, about 8,100 people were convicted for committing such offences and food safety authorities across the states had collected nearly ₹ 43.65 crore worth fine from the offenders. Tests were carried out on the parameters set by the FSSAI. 20,000 out of the total 65,000 samples failed the test in 2018-19. During 2017-18, over 24,000 samples out of 99,000 did not conform to the norms and during 2016-17, the number of failed samples was more than 18,000 out of the total 78,000 that were tested.

Reasons for rejection of samples by FSSAI
Food adulteration is not a rare occurrence. A simple Google search will show the alarming number of cases of adulteration being reported regularly by all leading national newspapers.
This is not a problem exclusive to India either. Globally, approximately 57 % of people have developed health problems due to ingestion of adulterated and contaminated foods. It is estimated that around 22 % of foods generated are adulterated every year.
Most Common Adulterants in India
| FOOD ARTICLES | ADULTERANTS | HARMFUL EFFECTS |
| Bengal Gram dhal & Thoor Dhal | Kesari dhal | lathyrism , cancer |
| Tea | Used tea leaves that are coloured with agents like tartrazine, Bismarck brown, potassium blue, turmeric, indigo, plumbago | Liver Disorder |
| Coffee Powder | *Tamarind seed *date seed powder *Chicory powder |
Diarrhoea, Nausea, vomiting, gastric irritation. |
| Milk | *Unhygienic Water *Formalin is a preservative that improves the shelf life of milk and saves on refrigeration costs. *Starch prevents milk from curdling. *Glucose, sugar and salt are added to thicken milk that has been diluted with water. *Detergents restore the foaminess of milk that is reduced after dilution |
Cancer, Diarrhoea, Nausea, vomiting, gastric irritation. |
| Wheat and other grains (Bajra) | Ergot (a fungus producing poisonous alkaloids) | Poisoning causes convulsions and gangrene. |
| Sugar | Chalk powder | Diarrhoea, Nausea, vomiting, gastric irritation, bowel obstruction |
| Black pepper powder | *Papaya Seeds *Buckwheat *Millet seed |
Stomach, liver problems, miscarriages |
| Mustard powder | Argemone seeds | vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, swelling of limbs, erythema, pitting edema, and breathlessness |
| Asafoetida | *galbanum *colophony resin *red clay, sand, stones *gypsum |
Dysentery |
| Turmeric powder | *Yellow aniline dyes *Non-permitted colourants like metanil yellow, *Tapioca starch |
Cancer and stomach disorders |
| Chilli powder | *Brick powder *saw dust *artificial colours |
Stomach problems, Cancer |
Laws to Protect You

Food adulteration is illegal and a legally punishable offence. The Constitution has laws that protect you against it.
The Food Safety and Standards (FSS) Act, 2006 consolidates the laws relating to food and established the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) to lay down science-based standards for articles of food and to regulate their manufacture, storage, distribution, sale and import, to ensure availability of safe and wholesome food for human consumption and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
Food adulteration is governed by the Prevention of Food Adulteration Act, of 1954. If any food operator sells, distributes, imports or stores any food article which is adulterated, he is liable under section 16 the Act and can be punished with imprisonment of 6 months, with a fine of Rupees 1000 under section 272 of IPC. The punishment could be extended, depending on the grievousness of the act.
What Can You Do
When a food article is found to be adulterated there is a 3-tier complaint redressal system where a consumer can complain:
- 1st tier is the shopkeeper or manufacturer from where a consumer has purchased food or drink for consumption.
- 2nd tier is the Local Health Authority of the District or the Commissioner of Food Safety of the State/ Union Territory.
- 3rd tier is the Consumer Forum.
Consumers can connect to FSSAI through various channels and register their complaints and feedback about food safety issues related to adulterated food, unsafe food, substandard food, labelling defects in food and misleading claims & advertisements related to various food products.
Channels through which consumers can connect with FSSAI are:

- Helpline (Toll-Free)- 1800112100
- Website: https://foodlicensing.fssai.gov.in/cmsweb/
- Email: Compliance@fssai.gov.in
- WhatsApp / SMS: 986868 6868
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fssai/
- Twitter : https://twitter.com/fssaiindia
- Walk-in with a prior appointment
- GAMA portal for misleading claims and advertisements: https://gama.gov.in/Default.aspx
- CPGRAM portal : https://foscos.fssai.gov.in/consumergrievance/
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest 

















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *