Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured, cell-based, or cultivated meat, is a groundbreaking innovation in food technology that offers an ethical and sustainable alternative to traditional meat production. Unlike plant-based substitutes, lab-grown meat is real meat developed from animal cells without the need for raising or slaughtering animals. Scientists believe this advancement could address pressing concerns related to animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and food safety. Although lab-grown meat is not yet widely available, ongoing research and technological improvements indicate that it could soon transform the global food system and become a mainstream dietary option.
What Is Lab-Grown Meat?
Lab-grown meat replicates the structure, texture, and taste of conventionally farmed meat by culturing animal cells in a controlled environment. This innovation can reduce reliance on factory farming, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and offer safer, customizable meat options. However, researchers must overcome challenges like cost, scalability, and public acceptance before it becomes widely accessible. Ongoing scientific advancements continue to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of lab-grown meat, positioning it as a promising solution for the future of food.
How Is Lab-Grown Meat Made?
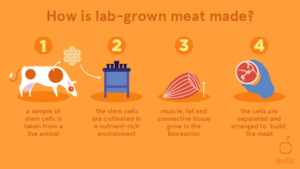
The process of cultivating meat in a lab involves four key steps:
- Cell Collection – Scientists extract stem cells from a live animal, allowing them to develop into muscle, fat, and connective tissue.
- Cell Culturing – Scientists place the collected stem cells in bioreactors and nourish them with a nutrient-rich culture medium that mimics an animal’s body, promoting cell multiplication and growth.
- Tissue Formation – Scientists adjust the culture medium to trigger cell differentiation, ensuring the formation of muscle fibres, fat, and connective tissues—the essential components of meat.
- Scaffolding – Scientists arrange the cells on an edible scaffold to create structured meat like steak or chicken breast, providing texture and structure. However, replicating the complexity of natural meat remains a challenge.
Advantages of Lab-Grown Meat
Lab-grown meat offers several potential benefits:
- Animal Welfare – Eliminates the need for large-scale animal farming and slaughter, making it a cruelty-free alternative.
- Environmental Sustainability – Reduces land, water, and feed requirements while lowering methane emissions associated with traditional livestock farming.
- Food Safety – Minimizes the risk of contamination from pathogens like E. coli and Salmonella, commonly found in conventionally farmed meat.
- Customization of Nutritional Content – Scientists can modify the fat content and enhance it with essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids or vitamin B12.
- Antibiotic-Free Meat – Unlike farm animals that often receive antibiotics to prevent infections, lab-grown meat eliminates the risk of antibiotic resistance due to excessive antibiotic use.
- Zoonotic Disease Prevention – Reduces the risk of disease outbreaks like avian flu and swine flu, which can spread from animals to humans.
Challenges and Safety Considerations
Despite its potential, lab-grown meat faces several challenges:
- High Production Costs – The cost of making lab-grown meat has decreased a lot since the first lab-grown beef burger was made in 2013 for around $333,000 (₹27 crore). However, producing it on a large scale is still expensive, making it difficult for common people to afford it.
- Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) Usage – Many early processes used FBS, a serum derived from calf fetuses. While companies are developing animal-free culture media, this remains a hurdle in achieving truly slaughter-free meat.
- Taste and Texture – Ground meat products like burgers are easier to create, but replicating complex cuts of meat with the same taste and texture remains difficult.
- Consumer Acceptance – Many people remain sceptical about lab-grown meat. Studies suggest that clear communication about its benefits and safety could improve consumer perception.
- Energy Consumption – While reducing land and water usage, lab-grown meat production requires significant energy. If fossil fuels power production, it may contribute to carbon dioxide emissions, offsetting some environmental benefits.
- Potential Health Risks – Concerns exist about the uncontrolled growth of lab-cultured cells. Researchers must ensure that the cellular growth process does not introduce any long-term health risks to consumers.
Regulatory Status and Availability
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) have approved some lab-grown meat products for human consumption. In 2022, Upside Foods became the first company to receive approval for its cultivated chicken. However, as of early 2024, lab-grown meat is not yet available in U.S. grocery stores.
Singapore was the first country to approve and sell lab-grown meat, setting a precedent for others. The European Union has yet to approve it, though the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is reviewing applications. Meanwhile, the UK has taken a unique step by approving lab-grown meat for pet food. In 2025, London-based Meatly launched the world’s first cultivated chicken dog treats, available in select stores.
In India, lab-grown meat research is still in its early stages, led by institutes like the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) and start-ups like Clear Meat. The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has yet to establish specific regulations. With concerns over food security, sustainability, and animal welfare, India is closely monitoring global developments. However, consumer perception and religious dietary considerations will likely influence its future adoption.
Conclusion
Lab-grown meat represents a promising solution to many ethical, environmental, and food safety issues associated with traditional meat production. It is cruelty-free, potentially healthier, and can be customized to meet specific dietary needs. However, high production costs, regulatory hurdles, and consumer perception remain significant challenges. As science and industry progress, lab-grown meat could play a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable food.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest 


















