The food industry prioritizes food safety and longer shelf life. Microbial contamination often causes spoilage and foodborne illnesses, making it a key concern. To address this, manufacturers are using antimicrobial coatings as an innovative solution. These coatings inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms like bacteria, mold, and fungi. They reduce contamination risks while preserving product quality, offering dual benefits—improved food safety and longer shelf life. This article explains how antimicrobial coatings work, highlights their key advantages, explores real-world applications, and discusses the challenges they present in the food sector.
What Are Antimicrobial Coatings?
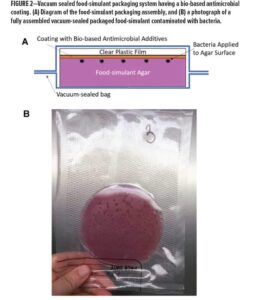
Manufacturers apply antimicrobial coatings to food and packaging materials to stop harmful microbes from growing. These coatings use natural or synthetic agents to kill or inhibit bacteria, fungi, and other pathogens. Common agents include silver nanoparticles, chitosan (derived from crustacean shells), and essential oils like oregano or thyme. Industries widely use these coatings on plastic films, trays, cartons, and even directly on fresh produce, meat, dairy, and baked goods. By slowing microbial growth, antimicrobial coatings help maintain freshness and extend the product’s shelf life.
How Do They Work?
Antimicrobial coatings protect food through four main mechanisms:
-
Slow Release: Some coatings gradually release antimicrobial agents, ensuring continuous protection during storage.
-
Surface Modification: Certain coatings alter the surface of food or packaging to make it harder for microbes to attach and grow.
-
Biofilm Prevention: They stop the formation of biofilms—clusters of microorganisms that are difficult to eliminate once established.
-
Direct Action: Some coatings kill microbes on contact by disrupting their cell walls or altering pH levels.
These combined actions help maintain food hygiene and quality from production to consumption.
Benefits for the Food Industry
Antimicrobial coatings bring several key benefits:
-
Extended Shelf Life: By slowing spoilage, these coatings keep perishable items like fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy fresh for longer.
-
Improved Safety: They reduce the risk of contamination by harmful bacteria such as E. coli, Listeria, and Salmonella, lowering the chances of foodborne illnesses.
-
Reduced Preservatives: As consumers seek cleaner labels, these coatings reduce the need for chemical additives, meeting the demand for more natural products.
-
Sustainability: Many coatings use biodegradable, plant-based materials, making packaging more eco-friendly.
-
Preserved Quality: Beyond safety, these coatings help retain food’s taste, texture, and nutritional value over time.
Real-World Applications
Antimicrobial coatings are already being used in a wide range of food categories:
-
Fresh Produce: Coatings on fruits and vegetables like apples and leafy greens delay spoilage during transport and storage.
-
Meat & Seafood: Raw meat and seafood benefit from reduced bacterial growth, making them safer and giving them a longer shelf life.
-
Food Packaging: Coated films and containers protect food from external contaminants and maintain freshness.
-
Dairy Products: Items like cheese and yogurt stay fresher, with reduced spoilage and bacterial growth.
-
Baked Goods: Bread and pastries are shielded from mold, cutting waste and reducing the need for artificial preservatives.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their promise, antimicrobial coatings face a few hurdles:
-
Cost: High-quality coatings, especially those using silver nanoparticles or advanced materials, can be expensive, raising production costs.
-
Consumer Perception: Some consumers may be wary of “invisible” technologies or synthetic chemicals, even if they’re safe. Transparency and education are key.
-
Regulatory Approval: Coatings must meet safety standards and gain regulatory clearance (e.g., FDA approval), which can delay rollout.
-
Durability: Environmental factors like humidity, light, or heat can reduce coating effectiveness over time, so stability must be ensured throughout the product’s life.
Conclusion
Antimicrobial coatings are proving to be a powerful tool in enhancing food safety and extending shelf life. They actively combat spoilage and contamination, offering manufacturers a cleaner, more sustainable way to preserve food. While challenges like cost and regulation exist, the benefits—longer freshness, reduced preservatives, and safer food—make them an increasingly valuable innovation in modern food systems. As research continues and consumer awareness grows, antimicrobial coatings are set to play a bigger role in the future of food protection.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest 


















