As food security becomes an increasingly urgent global issue, understanding and applying food preservation techniques is essential. According to the World Food Programme, food waste is a staggering problem, with approximately $400 billion worth of food lost annually from harvest to retail. Additionally, about 17% of food is wasted at the consumer level. These figures underscore the pressing need to reduce food loss. Food preservation not only helps tackle waste but also plays a key role in ensuring food security, particularly in countries like India, where diverse climates and the rapid spoilage of perishable foods make preservation practices crucial. This article explores the significance of food preservation, its methods, and the societal benefits it offers.
Why Preserve Food?
Food preservation serves several essential purposes. The primary goal is to extend the shelf life of perishable items, ensuring a steady food supply even during periods of scarcity. By preserving food, we can enjoy seasonal produce throughout the year, reducing the risk of food shortages. Furthermore, preservation helps maintain the nutritional value of food, ensuring it remains safe and healthy to consume.
At its core, food preservation aims to maintain the flavour, texture, and nutritional quality of food while preventing spoilage. Different preservation techniques help store food safely, reduce environmental impact, and optimize resource use. Importantly, these methods contribute to food security by reducing reliance on fresh produce, which may not always be readily available.
Food Preservation in India: A Cultural Necessity
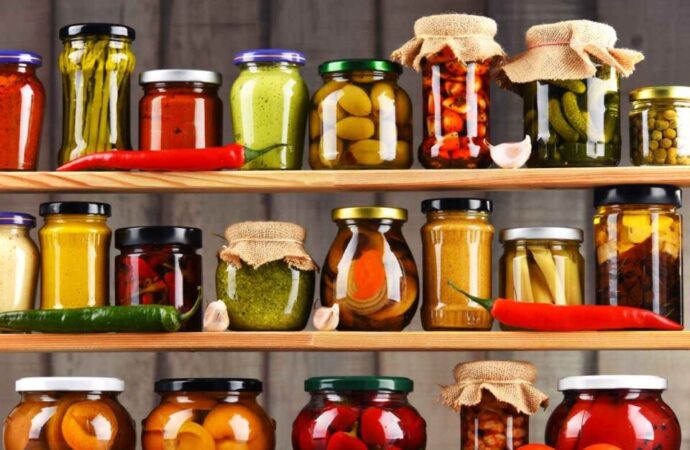
In India, food preservation is of particular importance due to the country’s diverse climates and the rapid spoilage of many foods in hot, humid conditions. Traditional methods such as drying, salting, and pickling have been used for centuries to extend the shelf life of food. Techniques like fermentation, passed down through generations, play a crucial role in preserving seasonal foods. This combination of traditional knowledge and modern practices ensures access to safe, nutritious food even in times of scarcity.
Common Food Preservation Methods
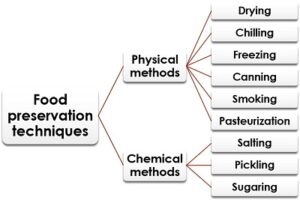
Several methods are used to preserve food, each suitable for different types of food and storage needs. Below are some of the most widely used techniques:
- Canning: Canning involves sealing food in airtight containers and heating them to destroy harmful microorganisms. This method is ideal for preserving fruits, vegetables, meats, and sauces. The vacuum seal created during the heating process prevents new bacteria from entering.
- Freezing: Freezing slows down the activity of enzymes and bacteria by storing food at low temperatures. This method preserves the food’s nutritional quality for months or even years. Freezing is particularly effective for fruits, vegetables, and meats.
- Drying: Drying removes moisture from food, which prevents the growth of bacteria, yeast, and moulds. This ancient method is effective for preserving fruits, vegetables, and meats. Dehydrated foods retain most of their nutrients and can be stored for extended periods without refrigeration.
- Fermentation: Fermentation uses microorganisms to convert sugars into alcohol or acids. This process not only preserves food but also enhances its nutritional value by creating beneficial bacteria. Common fermented foods include yoghurt, sauerkraut, and kombucha.
- Pickling: In pickling, food is immersed in an acidic solution or brine, which prevents bacterial growth. This method is commonly used for preserving cucumbers, onions, and other vegetables.
Benefits of Food Preservation
Food preservation offers numerous advantages, ranging from improved food security to promoting sustainability. Some key benefits include:
- Enhanced Food Security: Preservation techniques ensure access to food year-round, even when seasonal supplies are limited.
- Nutritional Retention: Proper preservation methods help retain food’s nutritional value, making it a reliable source of healthful nourishment.
- Economic Savings: Preserving food allows individuals and families to save money. Bulk purchases and proper storage reduce the need for frequent grocery trips and lessen reliance on fresh produce.
- Sustainability: Food preservation reduces the demand for continuous food production and transportation, thereby lowering the carbon footprint associated with food consumption.
Practical Tips for Home Food Preservation
Preserving food at home can be both cost-effective and rewarding. Here are some tips to get started:
- Start Small: Begin with simple methods like freezing or drying before progressing to more advanced techniques such as canning.
- Use Quality Ingredients: Always start with fresh, high-quality produce for the best preservation results.
- Understand the Process: Each preservation method has specific steps that ensure both safety and effectiveness. Take time to learn about the process to maintain quality.
- Label Everything: Label preserved foods with the date and contents to ensure proper use before spoilage.
Conclusion
Food preservation is an indispensable practice that offers multiple benefits, from extending the shelf life of food to reducing waste and ensuring food security. By adopting various preservation techniques, we can guarantee a safe, nutritious, and sustainable food supply year-round.
As the world faces challenges like hunger, food scarcity, and environmental degradation, understanding and implementing food preservation methods can have a lasting impact. Whether through traditional techniques like fermentation and pickling or modern practices like freezing and canning, food preservation remains fundamental to sustainable living and responsible consumption. By reducing food waste and the environmental impacts of discarded food, we can work toward a more sustainable future.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest