The merits and demerits of milk has been a topic of debate for at least the past thousand years. In the United States, milk was one of the first foods ever to be tested in a laboratory, and in present times, it is one of the most regulated food in most nations worldwide.
How Important is Milk in Your Diet?
Milk consumption has been a hotly debated subject for years with contradiction and controversy surrounding its acclaimed benefits.
One particular study in Sweden established that high milk intake was associated with higher mortality in men and women. While this study is just one among many contradicting ones, there are other acclaimed benefits to consuming milk. During adulthood, consumption of milk is especially beneficial since it improves bone health and can help prevent osteoporosis.
It is also rich in potassium and protein, both of which can help with muscle repair and in maintaining blood pressure. These benefits however, vary depending on a number of factors and must be interpreted cautiously.
| Nutrients | Low-Fat Milk | Fat-Free Milk | Full-Fat Milk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 102 | 86 | 146 |
| Fats | 2mg | 0mg | 8 mg |
| Cholesterol | 12mg | 5mg | 24mg |
| Sodium | 107mg | 128mg | 98mg |
| Carbohydrates | 13mg | 12mg | 13mg |
| Sugar | 13mg | 12mg | 13mg |
| Proteins | 8mg | 8mg | 8mg |
Why is milk so controversial?
Studies over the years have shown conflicting results in the acclaimed benefits of milk. While some studies show that milk must be consumed for better bone density since it contains calcium, other contradictory ones show that there is no significant difference in fracture rates between people who consume negligible and almost too much milk in their diets.
Additionally, the claim that milk builds strong bones has been contradicted by some studies that show that those who consume more milk actually had more bone fractures than those who consumed less. Data from such studies do not support the hypothesis that a higher consumption of milk and its associated calcium rich foods especially by adult women, protects against hip or forearm fractures.
Despite the industry’s constant assurances that milk is a dietary staple, there is very little scientific evidence that this is the case. While milk is undoubtedly a rich source of calcium, protein and vitamin D, these nutrients can easily be found in other foods.
Adulteration of milk

Equipment for testing milk for adulterations in India (photo credit: ILRI).
Another reason why milk is controversial is that, it is one of the most adulterated foods in the world.
India is the largest exporter of milk, however, there is a significant disparity between the production and consumption of milk. This vast gap is being misused and manipulated by the business of milk adulteration.
70% of milk samples acquired by the food safety authority across the country did not meet the standards. One of the most popular milk adulterant was discovered to be water, which significantly lowers milk’s nutritional value.
It has also been found that in most cases, contaminants like glucose, starch, urea, formalin and even detergent are used as adulterants for the purpose of increasing the viscosity, thickness and shelf-life of milk.These adulterants are poisonous and cause irreparable organ damage.
Detergents in milk cause food poisoning and gastrointestinal issues, according to an earlier investigation by the Indian Council of Medical Research, while other synthetic substances cause impairments, heart problems, cancer, and even death. The immediate impact of drinking urea, caustic soda, or formalin-laced milk is gastroenteritis, but the long-term repercussions such as impairments, heart problems, cancer and even death in some cases, are significantly more devastating.

Which milk is the best?
For human adults, according to research, good old cow milk remains the healthiest type of milk, as long as it can be digested without any underlying issues like lactose intolerance.Studies show that consumption of cow’s milk can lead to greater bone density and muscle mass, and lower the risk of childhood obesity, stroke, diabetes and cardiovascular disease; however, the evidence for such claims are rather slim.
Basic human mechanics explains that a higher consumption of milk which might lead to the development of longer bones increases the chances of fractures since longer bones are more prone to breakage than shorter ones. Additionally, around 1 in 10 children develop some sort of a reaction when they consume cow’s milk and related dairy products, and this could be because they are lactose intolerant or have a milk allergy.
The next best alternative to cow milk, nutritionally speaking, is goat milk. It has a higher protein content and is widely observed to be less allergenic. Studies show that goat milk is an excellent substitute in children older than 2 years old. The protein content in goat milk is also seen to be more similar to human breast milk than cow milk.
| (Per 8 fl. ounces / 236.5 ml) | Calories | Carbohydrates (total) | Sugars | Fat (total) | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human milk | 176 | 16.8 g | 16.8g | 10.4 g | 2.4 g |
| Cow’s milk (whole) | 150 | 12 g | 12 g | 8 g | 8 g |
| Cow’s milk (skim) | 80 | 12 g | 12 g | 0 g | 8 g |
| Goat’s milk | 170 | 9 g | 11 g | 10 g | 9 g |
| Almond milk (unsweetened) | 40 | 1 g | 0 g | 3 g | 2 g |
| Soy milk (unsweetened) | 80 | 4 g | 1 g | 4 g | 7 g |
| Rice milk (unsweetened) | 120 | 22 g | 10 g | 2 g | 0 g |
| Coconut milk beverage (unsweetened) | 50 | 2 g | 0 g | 5 g | 0 g |
Plant based milk
For vegans, soy milk is the best option since it has high protein content. And for those with milk allergies, almond milk seems to be the safest bet. These plant-based milk options can have their protein content improved by adding a little bit of whey protein powder which provides protein levels similar to that of cow milk, minus the allergenic effects. While coconut milk is a popular cooking ingredient, it is rarely used as a milk substitute since its nutrient content is inadequate. Another alternative for patients who are extremely allergic to milk and its products is rice milk. However, it has an extremely poor nutritional profile and it cannot be treated as an adequate milk alternative to cow milk since it can lead to severe malnutrition
Ethical issues of milk
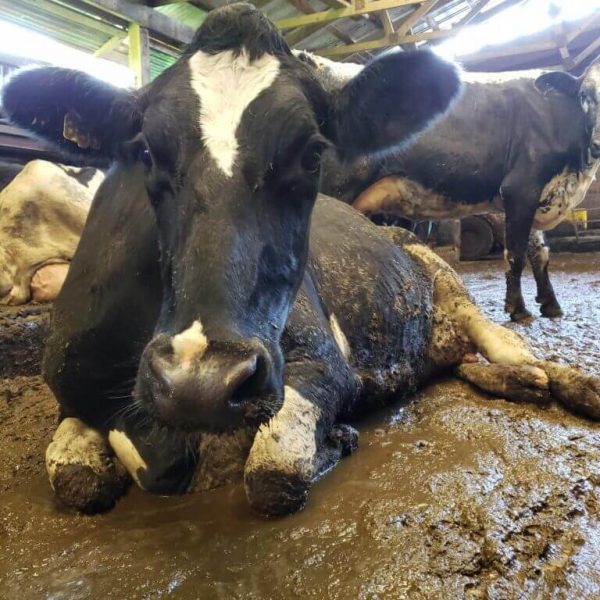

For cows to produce milk, they are repeatedly impregnated and separated from their new-born calves within just 24 hours of giving birth, which causes extreme distress, and are put under torturous conditions to produce more than 20,000 pounds of milk each year. Besides this, the dairy farming industry has a detrimental effect on the planet. According to WWF’s estimate, of approximately 270 million dairy cows in the world, the average cow uses around 5000 gallons of water a day. Besides this, cows also produce excessive amounts of greenhouse gases, which have a devastating effect on the planet.
The bottom line
Milk appears to be neither a hero nor a villain when it comes to general health advantages. While most people still prefer it for its health and nutritional benefits, many individuals are looking for alternatives to this household staple. In an attempt to save cows from misery of the ways of dairy farming, many individuals are switching to plant-derived milk alternatives that provide the necessary calcium, zinc, iron, protein and vitamins but do not contain any cholesterol. While the line between the benefits and drawbacks of consuming milk is blurry, it is ultimately one’s personal choice to consume milk or even what type of milk, after considering factors such as the environment, and own health.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest 


















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *