Artificial sweeteners have become widely adopted in the food and beverage markets, with manufacturers promoting them as healthier alternatives to sugar. People commonly use these sweeteners in diet sodas, protein bars, baked goods, and “sugar-free” snacks. These sweeteners serve as key ingredients in foods designed to reduce calories and support weight management. However, as their popularity grows, people continue to debate their safety, potential side effects, and long-term health effects. This article explores the science behind artificial sweeteners, their benefits, common types, and the concerns surrounding their consumption.
What Are Artificial Sweeteners?
Artificial sweeteners, also known as sugar substitutes, are synthetic chemicals that mimic the sweetness of sugar without adding calories. Manufacturers often call them “intense sweeteners” because they are thousands of times sweeter than table sugar. This allows producers to use only a small amount to achieve the desired sweetness. As a result, they appear in a variety of low-calorie or “diet” foods and beverages. The main appeal of artificial sweeteners is that they provide sweetness without contributing to a product’s calorie count. This makes them especially popular among individuals who want to manage their weight or control their blood sugar levels.
Common Types of Artificial Sweeteners and How They Are Made
In India, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has approved various synthetic and plant-derived artificial sweeteners for use in diet foods, beverages, and sugar-free products. These sweeteners are popular because they provide sweetness without adding calories. Here’s an overview of some common types and their production processes:
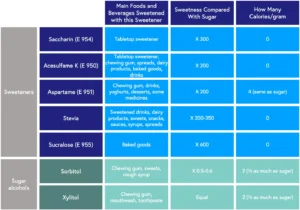
How Do Artificial Sweeteners Work?
Artificial sweeteners bind to sweet taste receptors on the tongue, triggering the brain to perceive sweetness. These sweeteners are much sweeter than sugar, so manufacturers need only a small amount to achieve the desired sweetness. This intense sweetness is what gives them their “intense” label. The effectiveness of artificial sweeteners lies in their ability to provide sweetness without the calories or carbohydrates found in sugar. While sweeteners like saccharin and aspartame contain no calories, others, such as sugar alcohols, provide small amounts of calories—though still far fewer than sugar.
The Benefits of Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners offer several potential benefits due to their ability to provide sweetness with minimal caloric impact. These include:
- Weight Management: Artificial sweeteners help people reduce calorie intake, which is essential for weight control. Since they are calorie-free or very low in calories, they satisfy sweet cravings without adding excess calories.
- Diabetes Management: For individuals with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is crucial. Most artificial sweeteners do not affect blood glucose, making them a safer alternative to regular sugar.
- Dental Health: Unlike sugar, which contributes to tooth decay, artificial sweeteners do not feed the bacteria in the mouth that cause cavities, making them less harmful to dental health.
Health Risks of Artificial Sweeteners: A Summary
The FSSAI deems artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, and stevia safe when consumed in moderation. However, concerns about their long-term effects persist. Potential risks include:
- Metabolic Issues: Some research suggests that artificial sweeteners may affect insulin resistance, potentially raising the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Gain: Artificial sweeteners can increase cravings for sweet foods, which may lead to overeating and weight gain.
- Digestive and Neurological Effects: Excessive consumption of some artificial sweeteners can cause digestive discomfort (like bloating), and some people report headaches. However, studies on neurological effects remain inconclusive.
As health awareness increases, many are choosing natural sweeteners like stevia, monk fruit, and allulose over synthetic options. While considered healthier and more “natural,” these sweeteners can be expensive, less stable in cooking, and may have a bitter aftertaste. Despite these downsides, they remain popular for their organic appeal.
Conclusion
Artificial sweeteners play a key role in modern food production by allowing people to enjoy sweetness without the calorie load of sugar. They offer benefits like weight control, diabetes management, and better dental health. However, concerns about their long-term safety continue to linger. As research evolves, consumers must stay informed about both the benefits and potential risks of artificial sweeteners. Whether opting for synthetic or natural alternatives, moderation remains essential for making healthy dietary choices.
As with all food ingredients, understanding what you consume and how it affects your body is crucial for making the right choices for your health,
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest 


















