As food supply chains become more complex and consumers increase their awareness of food safety, businesses must adopt robust frameworks to manage potential risks effectively. In this context, “HACCP,” or Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points, emerges as a crucial term. HACCP serves as a globally recognized food safety management system that ensures the food we eat is both safe and delicious.
When businesses implement a HACCP program effectively, they significantly reduce customer complaints and recalls. This system identifies and controls hazards from raw materials, facility processes, and human error. By taking a proactive approach, businesses can spot risks early and take measures to manage them, ensuring food products remain safe from farm to table.
What is HACCP?
HACCP helps businesses systematically identify and control potential hazards throughout the food production process. This comprehensive system addresses biological, chemical, and physical risks, starting from raw material production and procurement to the distribution and consumption of the finished product. HACCP analyzes where hazards arise and establishes targeted measures to minimize these risks, ensuring safe food production and delivery.
To enhance its effectiveness, HACCP collaborates with essential prerequisite programs, such as pest control, hygiene, sanitation, traceability, and recall mechanisms. HACCP aims to prevent or substantially reduce food safety hazards by applying scientific principles to food processing and production. This approach not only ensures compliance with regulatory standards but also strengthens consumer safety. Read on to learn in detail about HACCP and its significance in the food industry.
The Importance of HACCP
HACCP plays a significant role in global food safety, and its importance can be distilled into several key points:
- Consumer Safety: HACCP primarily protects consumers from foodborne illnesses and contaminants, ensuring they enjoy safe food.
- Prevention Over Correction: HACCP emphasizes preventing hazards at specific points in the production process instead of relying solely on end-product testing. This proactive strategy significantly reduces the likelihood of unsafe food reaching consumers.
- Systematic Approach: HACCP provides a structured method for identifying potential hazards and implementing critical control points (CCPs), ensuring that no step in the production process is overlooked.
- Economic Benefits: Foodborne illnesses can lead to costly recalls, legal actions, and medical treatments. By minimizing contamination risks, businesses avoid these expenses and protect their reputations.
- Compliance and Trade: Many international markets require HACCP certification as a prerequisite for trade. Implementing HACCP allows food producers to access valuable global market opportunities.
- Streamlined Processes: By understanding and monitoring CCPs, businesses can create more efficient production processes, reduce waste, and improve overall productivity.
- Foundation for Other Standards: HACCP often serves as a foundation for other food safety standards and certifications, simplifying the process for businesses to achieve additional certifications if they adhere to HACCP principles.
- Boosts Consumer Confidence: When businesses follow HACCP standards, they enhance consumer trust in their brands and products, reassuring customers that they prioritize food safety.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular reviews and updates required by HACCP ensure that food safety management processes remain current and evolve alongside changing technologies and risks.
- Holistic View of Safety: HACCP adopts a comprehensive approach to food safety by considering a wide range of hazards—biological, chemical, and physical—ensuring thorough coverage.
The Seven Principles of HACCP
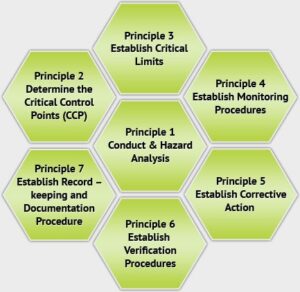
HACCP relies on seven fundamental principles that guide food businesses in establishing effective food safety management systems. Each principle acts as a crucial building block, helping organizations ensure food safety and comply with relevant regulations.
- Conduct a Hazard Analysis: The first step requires businesses to thoroughly examine each stage of the food production process to identify potential hazards. This analysis should cover all aspects, including raw materials, processing methods, equipment, and personnel practices. By understanding the specific hazards relevant to their operations, businesses can take informed steps to mitigate risks.
- Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs): After identifying hazards, businesses must pinpoint where they can apply control measures to prevent, eliminate, or reduce hazards to acceptable levels. CCPs represent critical points in the process where control can be applied, and failure to do so could lead to unacceptable health risks.
- Establish Critical Limits: For each CCP, businesses must set specific and measurable critical limits to ensure effective hazard control. These limits, based on scientific research, may include temperature thresholds or pH levels.
- Establish Monitoring Procedures: To ensure compliance with critical limits, businesses must implement monitoring procedures. This involves conducting regular checks and documenting conditions at each CCP to verify that processes operate within established parameters.
- Establish Corrective Actions: If monitoring indicates that a critical limit has not been met, businesses must prepare to implement corrective actions. These may include reprocessing products or recalling items from distribution.
- Establish Verification Procedures: Verification procedures ensure that the HACCP system functions as intended. This may involve conducting audits, tests, and record reviews to confirm that the system effectively manages food safety risks.
- Establish Record-Keeping and Documentation Procedures: Maintaining thorough documentation is vital for demonstrating compliance with food safety regulations and the effectiveness of the HACCP plan. Records should include hazard analyses, monitoring activities, and corrective actions taken.
Key Takeaways
HACCP represents a proactive, systematic approach to food safety that remains vital in today’s global food supply chain. By adhering to the principles of HACCP, food businesses not only ensure compliance with regulations but also protect consumers and build trust in their brands. As food safety risks continue to evolve, businesses’ commitment to HACCP principles will remain essential for fostering a safe and reliable food supply.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest 


















