In today’s fast-paced world, consumers demand convenience, food safety, and sustainability. As the need for healthy, easy-to-use, and long-lasting food products grows, aseptic foods are playing an increasingly vital role in the food industry. From ready-to-eat meals to dairy products that stay fresh longer without refrigeration, aseptic foods revolutionize modern food processing. Technological advances drive this sector forward, enhancing nutrient retention, improving flavour preservation, and promoting eco-friendly packaging solutions.
As the global population grows and food security becomes a more urgent issue, aseptic foods provide a crucial solution to hunger, food waste, and the challenges of feeding remote populations. Their ability to deliver safe, nutritious, and long-lasting food makes them a cornerstone of both current and future food production systems. This article explores how aseptic foods are produced, the types of products that benefit from aseptic processing, and how they contribute to food safety, quality, and sustainability.
What Are Aseptic Foods?
Aseptic foods are products that undergo a specialized processing technique designed to eliminate harmful microorganisms while preserving the food’s quality, flavour, and nutritional content. The term “aseptic” means “free from contamination,” and this processing method ensures that food is sterilized and packaged in a sterile environment, allowing it to remain safe for consumption without refrigeration for extended periods.
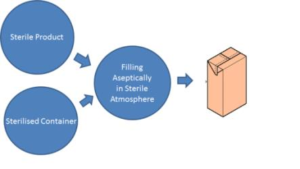
The core principle behind aseptic foods is aseptic processing, which combines heat treatment and sterile packaging. The process involves two critical steps:
- Heat Treatment: Manufacturers subject the food to high temperatures, typically above 85°C (185°F), to kill harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, and moulds. The duration and intensity of the heat treatment depend on the type of food and the desired shelf life.
- Sterile Packaging: After heat treatment, manufacturers seal the food in sterile, air-tight packaging to prevent re-contamination. Materials such as foil, plastic, or laminated cartons protect the food from light, air, and moisture, ensuring its preservation.
Types of Aseptic Foods
Aseptic processing is widely used for food products that require extended shelf life without refrigeration. Some of the most common examples include:
- UHT Milk: Ultra High Temperature (UHT) milk is one of the most recognized aseptic products. The milk undergoes rapid heat treatment, sterilizing it while retaining its taste and nutritional value. UHT milk can stay at room temperature for months, making it ideal for areas with limited refrigeration options.
- Fruit Juices and Beverages: Manufacturers heat aseptic fruit juices to eliminate pathogens and preserve their fresh flavour. This process makes them convenient and portable, commonly packaged in juice boxes and other containers.
- Ready-to-Eat Meals: Manufacturers use aseptic packaging for meals like soups, curries, and stews. These meals are sterilized and sealed, allowing consumers to enjoy them without refrigeration while extending their shelf life for months.
- Tomato Paste and Sauces: Producers process tomato-based products, such as sauces and pastes, aseptically to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage, eliminating the need for preservatives.
- Infant Formula: Aseptic processing ensures that infant formula remains safe, nutritious, and free from contamination, all while not requiring refrigeration.
- Dairy Products: Beyond milk, aseptic processing is used for other dairy items like cream, butter, and yoghurt beverages. This method extends their shelf life while preserving their texture and flavour.
How Aseptic Processing Benefits Food Quality
Aseptic foods offer numerous benefits in terms of food safety, quality, and convenience. Here are the key advantages:
- Extended Shelf Life:
Aseptic processing significantly extends the shelf life of food products. Unlike traditional canning or refrigeration, aseptic foods last for months or even years without spoiling. This makes them ideal for distribution in regions with limited access to refrigeration or during crises when fresh food supply chains may face disruptions.
- Nutrient Retention:
Aseptic processing preserves the nutritional value of food products. The rapid heat treatment is gentler than traditional pasteurization or canning, helping retain essential vitamins and minerals, especially in fruit juices and dairy products.
- Better Taste and Freshness:
Aseptic foods undergo quick processing, which helps them retain more of their natural flavour and texture compared to products exposed to longer heating periods. For example, UHT milk and aseptic fruit juices taste fresher and more authentic than their pasteurized or canned counterparts.
- No Need for Refrigeration:
Aseptic foods stay at room temperature, making them convenient for areas with unreliable power sources or regions lacking refrigeration infrastructure. This feature also proves invaluable in disaster relief efforts, where non-perishable foods are essential.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging:
Many aseptic packages use recyclable materials like cartons, reducing the environmental impact of packaging waste compared to traditional metal cans, which take much longer to decompose.
Conclusion
Aseptic foods have revolutionized our approach to food safety, convenience, and nutrition. By using advanced processing methods to extend shelf life, preserve flavour, and maintain nutritional quality, aseptic foods have become a cornerstone of modern food production. As technology evolves, aseptic food processing will continue to improve, offering consumers safer, healthier, and more sustainable food options. As the global population grows and food security becomes a pressing issue, aseptic foods will play a vital role in addressing hunger, reducing food waste, and providing long-lasting, nutritious solutions to global food challenges.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest