As health awareness increases, more people actively seek ways to reduce their intake of refined sugar without giving up the sweet flavours they enjoy. This shift has driven widespread interest in natural sweeteners—plant-based or naturally derived alternatives that offer sweetness with fewer calories and potential health benefits. These sweeteners appeal to those managing weight, blood sugar, or following clean-eating lifestyles. But are they truly better than refined sugar? In this article, we define natural sweeteners, highlight the most popular types, explore their benefits, and explain what to watch for before making them a part of your daily diet.
What Are Natural Sweeteners?
Natural sweeteners come from plant or natural sources and sweeten foods and drinks without the processing or health risks associated with refined sugar or high-fructose corn syrup. Many cultures have used them in traditional diets for centuries. Unlike regular sugar, these alternatives often carry nutrients, antioxidants, or other health-promoting compounds. Since many natural sweeteners have a lower glycemic index and fewer calories, they help reduce blood sugar spikes and may support better overall health.
Common Natural Sweeteners Available in India
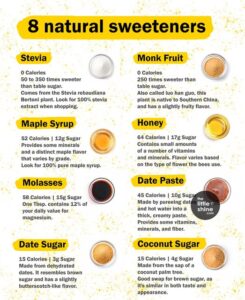
Here’s a look at some natural sweeteners that are commonly available in India. These options offer healthier alternatives to refined sugar, each with unique flavours and nutritional benefits suited to different tastes and dietary needs.
- Stevia
Stevia, derived from the Stevia rebaudiana plant, is a zero-calorie sweetener available in India in powder, tablet, and liquid forms. Up to 300 times sweeter than sugar, it’s ideal for diabetics as it doesn’t raise blood sugar levels. You can find it under several Indian brands in pharmacies, supermarkets, and online.
- Honey
Raw, unprocessed honey is widely available across India and used both as a sweetener and a home remedy. It contains antioxidants, enzymes, and trace minerals. Local varieties like wild forest honey and multiflora honey are popular and often used for soothing sore throats or boosting immunity.
- Jaggery
Jaggery is one of the most traditional and widely used natural sweeteners in India. Made by boiling raw sugarcane juice or palm sap, jaggery retains nutrients like iron, potassium, and magnesium. It’s available in solid, liquid, or powdered form and is a staple in Indian sweets, snacks, and beverages.
- Coconut Sugar
Coconut sugar, made from the sap of coconut palm trees, is becoming increasingly popular in India, especially among health-conscious consumers. It has a lower glycemic index than regular sugar and offers a mild caramel flavour, making it a good alternative for baking or cooking.
- Dates and Date Syrup
Dates are naturally sweet and nutrient-rich, containing fibre, potassium, and antioxidants. Whole dates, date paste, and date syrup are easily available in Indian markets. They’re often used in sweets, smoothies, and energy bars as a natural sweetener with added health benefits.
- Maple Syrup (Imported)
While not traditionally used in Indian cuisine, maple syrup is available in premium grocery stores and online. Imported from countries like Canada, it contains minerals like manganese and zinc. Due to its higher cost, it’s less commonly used but remains an option for those seeking alternatives to refined sugar.
- Monk Fruit Sweetener (Limited Availability)
Monk fruit sweetener is relatively new to the Indian market but is slowly gaining traction, particularly among those following keto or diabetic diets. It offers zero calories and does not affect blood sugar. Availability is mostly limited to health food stores and online retailers.
- Benefits of Natural Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners provide sweetness with fewer health risks. They often have a lower glycemic index, contain nutrients, and suit many healthy diets.
- Lower Blood Sugar Impact
Many natural sweeteners, such as stevia and monk fruit, do not raise blood sugar levels. People with diabetes or insulin resistance often turn to these options for safer sweetening.
- Fewer Empty Calories
Unlike refined sugar, which offers no nutritional value, sweeteners like honey and maple syrup provide small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
- Cleaner Ingredients
Natural sweeteners support whole-food and clean-eating lifestyles. They come from minimally processed sources and often avoid synthetic chemicals.
Dietary Flexibility
Many natural sweeteners suit vegetarian, vegan, paleo, and gluten-free diets, giving consumers multiple ways to sweeten foods without compromising their values.
What to Watch Out For
Despite their advantages, not all natural sweeteners are created equally. Consider the following:
-
Caloric Content: Sweeteners such as honey, maple syrup, and coconut sugar still contain sugars and calories. Excess intake can lead to weight gain or blood sugar issues.
-
Purity: Some “natural” products undergo heavy processing or contain artificial additives. Always read labels carefully.
-
Taste: Certain sweeteners, particularly stevia and monk fruit, can leave an aftertaste that takes time to adjust to.
-
Allergies: Some individuals may experience sensitivity or allergic reactions to specific plant-based sweeteners.
Conclusion
India offers a variety of accessible natural sweeteners—from traditional options like jaggery and honey to modern choices like stevia and coconut sugar. These alternatives can help you reduce your intake of refined sugar while still enjoying the sweetness in your daily diet. Whether you’re managing your blood sugar, following a specific diet, or simply choosing more natural foods, these sweeteners provide both taste and health benefits.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest 


















