Food allergies and food intolerances often get confused, but they have key differences that are important for your health. A food allergy occurs when your immune system overreacts to a food protein, triggering symptoms that can range from mild to life-threatening. On the other hand, food intolerance involves difficulty digesting certain foods, leading to discomforts like bloating, gas, or diarrhoea, but isn’t usually life-threatening. Understanding the differences between these two conditions helps you manage your symptoms better and make smarter dietary choices. Stay informed to keep your body happy and healthy!
What is a Food Allergy?
A food allergy is an immune system response to a particular food that the body mistakenly identifies as harmful. When a person with a food allergy eats or even comes into contact with the allergen, their immune system triggers a reaction. This response can vary from mild symptoms, such as hives, to more severe reactions like anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening.
Common food allergens include:
- Milk
- Eggs
- Peanuts
- Tree nuts
- Fish
- Shellfish
- Wheat
- Soybeans
- Sesame
Symptoms of Food Allergy
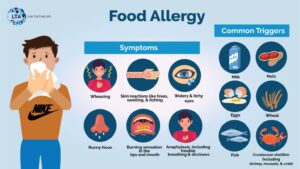
The symptoms of a food allergy include the following:
- Swelling of the face, lips, or throat
- Hives or rash
- Itchy skin
- Stomach pain or cramps
- Difficulty breathing
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
- Anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction, which requires immediate medical attention)
Anaphylaxis is an emergency and can be fatal without treatment, often requiring an epinephrine injection (EpiPen). Even trace amounts of an allergenic food can trigger a severe reaction.
What is Food Intolerance?
A food intolerance is a digestive issue where the body has difficulty processing certain foods. Unlike a food allergy, food intolerance doesn’t involve the immune system but rather an inability to properly break down a food due to enzyme deficiencies or sensitivities. It is usually less severe than an allergy, though it can still cause discomfort and digestive problems.
Common food intolerances include:
- Lactose intolerance: Difficulty digesting lactose, the sugar found in dairy products.
- Gluten intolerance: Sensitivity to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
- Histamine intolerance: Sensitivity to histamine found in aged, fermented, and preserved foods.
- Sulfite intolerance: Sensitivity to sulfites used in food preservation.
Symptoms of Food Intolerance
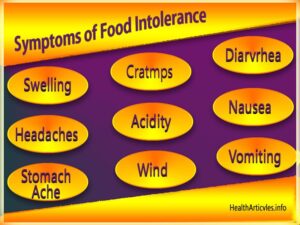
The symptoms of food intolerance include:
- Bloating
- Gas
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Nausea
- Fatigue
Food intolerances can vary in severity. While some people can tolerate small amounts of the triggering food, others may need to eliminate it from their diet to avoid symptoms.
Key Differences Between Food Allergy and Food Intolerance
Immune System Involvement:
- Food allergies involve the immune system, where the body mistakenly targets food proteins as harmful.
- Food intolerances involve the digestive system, typically due to enzyme deficiencies or sensitivities.
The severity of Symptoms:
- Food allergies can lead to severe, life-threatening reactions like anaphylaxis.
- Food intolerances usually cause discomfort but are not life-threatening.
Threshold:
- A food allergy can trigger a reaction even with a small amount of allergenic food.
- Food intolerance symptoms may depend on the quantity of the food consumed; small amounts may not always cause issues.
Treatment:
- Food allergies require strict avoidance of allergens and, in some cases, emergency treatments like epinephrine injections.
- Food intolerances can often be managed with dietary adjustments, enzyme supplements (e.g., lactase for lactose intolerance), or avoiding the triggering foods.
What About Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten. Unlike food intolerance, celiac disease involves the immune system, but it is not classified as a food allergy. While the symptoms are often gastrointestinal (like diarrhoea and abdominal pain), celiac disease can also cause joint pain, headaches, and other systemic issues. Unlike an allergy, celiac disease is not life-threatening in the immediate sense but can cause long-term damage to the intestines if left untreated.
How to Diagnose Food Allergies vs. Food Intolerances
If you suspect you have a food allergy or intolerance, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. They may recommend:
- Allergy testing (e.g., skin prick tests or blood tests) to identify allergens.
- Elimination diet to identify food intolerances by removing and gradually reintroducing suspected foods.
- Food challenge tests under medical supervision to confirm the diagnosis.
Managing Food Allergies and Intolerances
While there is no cure for food allergies or intolerances, both conditions can be managed effectively with the right approach.
- Food Allergies: The primary management strategy is complete avoidance of allergenic food. Always read food labels carefully, and be cautious when eating out or consuming pre-packaged foods. People with severe allergies should carry an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) in case of an emergency.
- Food Intolerances: Managing food intolerances typically involves adjusting your diet. For example, if you’re lactose intolerant, you can switch to lactose-free products or take lactase supplements. Gluten-free diets can help those with gluten intolerance, and enzyme supplements can assist with digestion.
Final Thoughts
The distinction between food allergies and food intolerances is crucial for effective health management. While food allergies can trigger life-threatening reactions, food intolerances typically lead to discomfort that can be managed with dietary changes. If you’re unsure whether you’re dealing with an allergy or intolerance, consulting a doctor or allergist is the best way to clarify your condition and develop a tailored treatment plan.
Understanding the differences between allergies and intolerances empowers you to make informed decisions about your health. By recognizing symptoms and seeking professional guidance, you can manage your condition and enjoy a balanced, worry-free lifestyle.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest 

















