Overview
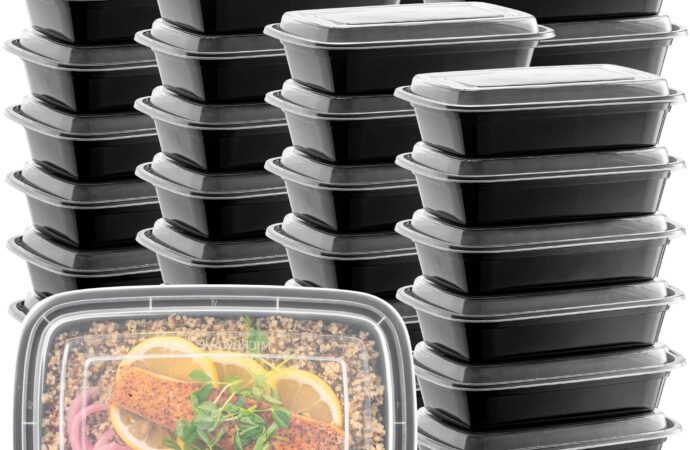
Black plastic containers are widely used for food delivery and storage due to their convenience, affordability, and durability. Many people reuse them, assuming they are safe for reheating food. However, black plastic often contains chemicals and recycled materials that can pose health risks.
Unlike transparent plastics, black plastic may include recycled electronics or industrial plastics. Manufacturers often add chemical flame retardants like decaBDE, which are not permanently bound and can migrate into food, especially when heated or in contact with fatty or acidic items. They can also contain BPA and phthalates, chemicals known to disrupt hormones and affect metabolic, reproductive, and cardiovascular health.
Health Risks
Heating food in black plastic increases the chance of chemical migration. Long-term exposure may accumulate harmful substances in the body. Research shows that a large proportion of black plastics contain toxic flame retardants, and microplastics from these containers may also add to the body’s toxic load. Children are especially vulnerable, as certain additives may affect neurological development.
Environmental Impact
Black plastic is difficult to recycle and releases toxic compounds like dioxins and furans when burned or discarded, posing risks to human health and the environment.
Safe Alternatives
- Use glass, stainless steel, or wooden containers for storing and reheating food.
- Avoid microwaving or heating food in black plastic.
- Switch utensils from black plastic to safer materials.
By adopting these practices, you protect your health, reduce chemical exposure, and support a safer, cleaner environment.
Source: Times Entertainment
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest