Most of you would say a big “no” to processed food. However, remember that a major portion of our daily food is processed. We consider food to be processed if it has undergone any changes from its original form. All chopped, canned, pasteurized, frozen, packed, dried, and cleaned goods fall under this category. This also includes foods with added flavours, sugar, salt, and preservatives. A few examples include fruits, vegetables, breakfast cereals, fresh bread, hams, and sausages.
Why do people process food? It increases the quality and shelf life of perishable food products. This, in turn, increases their nutritional value and accessibility.
You might be curious to know more about processed food. It comes in different categories, such as minimally processed or unprocessed, processed culinary ingredients, processed foods, and ultra-processed or heavily processed foods. Among them, you will find many healthy food items, while a few can be harmful to your health. Read on to learn more about the various categories of processed food, its advantages, and harmful effects.
Categorizing Processed Foods
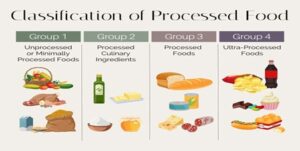
Classification of Processed Food
Minimally Processed Food
This category includes food items that are processed in such a way that there are very few alterations. Consuming minimally processed foods is considered healthy, as processing hardly makes any changes to their nutritional value.
- Covers the naturally edible portions of plants and animals.
- Undergoes slight processing to facilitate their storage, preparation, and consumption.
- Foods are fermented, vacuum-sealed, frozen, dried, refrigerated, and filtered to preserve their natural state for later consumption.
- Examples include fresh blueberries, lettuce, peeled carrots, cut or chopped vegetables, roasted nuts, walnuts, and ground coffee.
Processed Culinary Ingredients
These are food items that have been processed from their unprocessed state for use in the kitchen, as they cannot be eaten on their own.
- Includes culinary ingredients that are ground or milled in the kitchen to season dishes.
- Natural substances that undergo minor alterations.
- Undergo refinement, drying, milling, and pressing to facilitate their use in the kitchen.
- Added as flavour enhancers to food instead of being consumed on their own.
- Examples include sugar, oil, salt, butter, vinegar, and honey taken from combs.
Processed Foods
Lightly processed, these food items are made by combining ingredients from the other two groups. They will always have ingredients like salt, sugar, and oil added to them.
- Processed to improve their flavour and texture, thereby increasing their durability.
- Edible even in the absence of these enhancers.
- Requires minimal preparation time, as the majority just need two or three ingredients.
- Examples include cheese, bread, cakes, biscuits, breakfast cereals, canned fish, bottled vegetables and fruits, fruits in syrup, and meat products such as ham, sausage, and bacon.
Ultra-Processed Food Products
These are ‘junk’ foods made with a lot of sugar, salt, and oil, along with preservatives, antioxidants, and stabilizers. In short, ultra-processed food items contain many ingredients that are not found naturally.
- Undergo extensive processing.
- Ready-to-eat with minimal preparation time.
- Possess low fibre and nutritional content.
- Thickeners and artificial sweeteners are added to products in the previous group, along with salt, sugar, and fat to extend their shelf life and durability.
- Contains components derived from protein isolates, maltodextrin, invert sugar, whey, hydrogenated oils, casein, lactose, and gluten.
- Examples include snacks such as crisps and chips, sweetened breakfast cereals, packaged foods, frozen desserts like ice cream, and carbonated drinks.
How Beneficial is Processed Food
As mentioned above, processed food increases shelf life through processes such as sterilization and fermentation. Some of its other benefits include:
- Limiting food waste, which in turn benefits the environment and manufacturers.
- Processing techniques, like pasteurization, help in removing bacteria, thus enhancing food safety.
- Increases availability and variety of food through safe storage and transportation methods.
- Helpful during food crises when food needs to be transported and redistributed on a large scale.
Let us see how it helps:
- Cooking beans and lentils, as well as grinding grains into flour, makes food more soluble and accessible to the body.
- Caramelizing, adding flavours, food colouring, or thickeners alters the entire taste, texture, and colour of the food.
- Salad bags, pre-cooked food, and ready-to-eat options save time and effort.
- Frozen, sterilized, or canned vegetables and fruits maintain their freshness for a longer duration.
- Vacuum-packed meat stays fresh for a very long time.
- Cleaned and bagged spinach and lettuce are simple to prepare and consume.
- Fruits remain fresh and nutrient-rich if canned in their juice or water.
Is Processed Food Harmful to Health?
Processed food is the least favoured option among those who value health. Here are some of its harmful effects:
- Pre-packaged and processed foods are high in calories but low in nutrition.
- Canned in sugar syrups and containing high levels of sodium, constant consumption of processed food can lead to diseases such as diabetes, cancer, obesity, stroke and heart problems.
- Refined carbohydrates present in these processed foods lead to unpredictable insulin and sugar levels, as the body breaks down basic carbs quickly.
- Highly processed foods contain low fibre and fewer nutrients, leading people to consume them in excess.
- Ultra-processed food products contain unrecognizable artificial chemicals, flavourings, and texturizing agents. Manufacturers may not disclose the original contents.
- Processed foods are much easier to digest compared to unprocessed foods, leading our bodies to burn fewer calories during digestion.
Key Takeaways
It is impossible to avoid processed foods entirely, as they form an indispensable part of our lives. It would be smarter to choose minimally processed options, considering the drastic health hazards that ultra-processed food items pose.
Picking fresh food at the grocery store, understanding the ingredients better from labels while purchasing food, and including fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains in your diet can help maintain a balanced approach to nutrition.
 Food Manifest
Food Manifest